CHINA - 2021/04/24: In this photo illustration the Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer Li Auto, ... [+]
Chinese electric vehicle maker Li Auto’s (NASDAQ: LI) stock rallied by about 18% over the last two trading days, following the company’s Q1 2021 earnings release. While the results were reasonably strong, they weren’t exactly a blowout. Revenues marginally beat expectations, rising by over 4x year over year to RMB 3.58 billion ($545.7 million) although they declined by about 14% on a sequential basis as production was constrained by the ongoing chip shortage and the Chinese lunar new year holiday. Adjusted loss per share was also slightly wider than expected. However, the rally likely has to do with Li Auto’s outlook.
For Q2, Li Auto expects to deliver between 14,500 and 15,500 vehicles, marking a sequential increase of about 19% at the mid-point. The company expects to scale up deliveries even further from the month of September, noting that it is targeting the production of over 10,000 vehicles per month. [1] Now although we think this target looks very aggressive, considering that the company delivered an average of just about 4,200 vehicles per month over Q1, there are multiple trends that support higher deliveries in the coming months. Firstly, the company will commence deliveries of an updated version of its Li-One SUV from June. The vehicle will offer enhancements including a higher driving range and new active safety features. Secondly, the company is also looking to expand its sales network from about 75 stores currently to around 200 stores by the end of the year, significantly enhancing its market presence and reach. Moreover, the worst of the automotive semiconductor shortage is likely to be over in the near future, and the easing of component supply could also help the company scale up production.
Now despite the recent rally, Li Auto’s stock remains down by roughly 27% year-to-date. The company also remains the most reasonably valued of the three U.S.-listed Chinese EV stocks, trading at just about 7x projected 2021 revenues, compared to over 11x for rivals Nio and Xpeng. If the company is able to follow through on its aggressive targets, we think the stock could see a meaningful rally from current levels. Our analysis Nio, Xpeng & Li Auto: How Do Chinese EV Stocks Compare? compares the financial performance and valuation of the major U.S. listed Chinese electric vehicle players.
[5/21/2021] Nio, Xpeng, Li Auto: How Do Chinese EV Stocks Compare?
U.S. listed Chinese EV players Nio, Xpeng (NYSE: XPEV), and Li Auto (NASDAQ: LI) have underperformed this year, with their stocks down by roughly 30% each, since early January. So how do these stocks compare post the correction? While Nio and Xpeng remain pricier compared to Li Auto, they probably justify their higher valuation for a couple of reasons. Here is a bit more about these companies.
Our analysis Nio, Xpeng & Li Auto: How Do Chinese EV Stocks Compare? compares the financial performance and valuation of the major U.S. listed Chinese electric vehicle players.
Nio remains the most richly valued of the three companies, trading at about 10.5x forward revenue. Revenues are likely to grow by over 110% this year, per consensus estimates. Longer-term growth is also likely to remain strong, given the company’s wide product portfolio (it already has three models on the market), its unique innovations such as battery swapping, its global expansion plans, and investments into autonomous driving. Nio brand also has a lot more buzz, with the company viewed as the most direct rival to Tesla
Xpeng trades at about 10x projected 2021 revenues. Sales growth is projected to be the strongest among the three companies, rising by over 150% this year, per consensus estimates. Besides its higher projected growth, investors have been assigning a premium to the company due to its progress in the autonomous driving space. Xpeng currently sells the G3 SUV and the P7 sedan and its new P5 compact sedan is likely to hit the roads later this year. Although Xpeng’s gross margins have improved, rising to about 11% over Q1, versus negative levels a year ago, they are still below Nio’s margins.
Li Auto trades at just 6x projected 2021 revenues, the lowest of the three companies. Revenues are likely to roughly double this year, with gross margins standing at 17.5% as of Q4 2020 (the company has yet to report Q1 results). The lower valuation is likely due to the company’s focus on a single product - the Li Xiang ONE, an electric SUV that also has a small gasoline engine and also due to the fact that Li Auto is behind rivals in terms of autonomous driving tech.
[10/30/2020] How Do Nio, Xpeng, and Li Auto Compare
The Chinese electric vehicle space is booming, with China-based manufacturers accounting for over 50% of global EV deliveries. Demand for EVs in China is likely to remain robust as the Chinese government wants about 25% of all new cars sold in the country to be electric by 2025, up from roughly 5% at present. [2] While Tesla is a leader in the Chinese luxury EV market driven by production at its new Shanghai facility, Nio, Xpeng (NYSE: XPEV), and Li Auto (NASDAQ: LI) - three relatively young U.S. listed Chinese electric vehicle players, have also been gaining traction. In our analysis Nio, Xpeng & Li Auto: How Do Chinese EV Stocks Compare?we compare the financial performance and valuation of the major U.S. listed Chinese electric vehicle players. Parts of the analysis are summarized below.
Overview Of Nio, Li Auto & Xpeng’s Business
Nio, which was founded in 2014, currently offers three premium electric SUVs, ES8, ES6, and EC6, which are priced starting at about $50k. The company is working on developing self-driving technology and also offers other unique innovations such as Battery as a Service (BaaS) - which allows customers to subscribe for car batteries, rather than paying for them upfront. While the company has scaled up production, it hasn’t come without challenges, as it recalled about 5,000 vehicles last year after reports of multiple fires.
Li Auto sells Extended-Range Electric Vehicles, which are essentially EVs that also have a small gasoline engine that can generate additional electric power for the battery. This reduces the need for EV-charging infrastructure, which is currently limited in China. The company’s hybrid strategy appears to be paying off - with its Li ONE SUV, which is priced at about $46,000 - ranking as the top-selling SUV in the new energy vehicle segment in China in September 2020. The new energy segment includes fuel cell, electric, and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
Xpeng produces and sells premium electric vehicles including the G3 SUV and the P7 four-door sedan, which are roughly positioned as rivals to Tesla’s Model Y SUV and Model 3 sedan, although they are more affordable, with the basic version of the G3 starting at about $22,000 post subsidies. The G3 SUV was among the top 3 Electric SUVs in terms of sales in China in 2019. While the company began production in late 2018, initially via a deal with an established automaker, it has started production at its own factory in the Guangdong province.
How Have The Deliveries, Revenues & Margins Trended
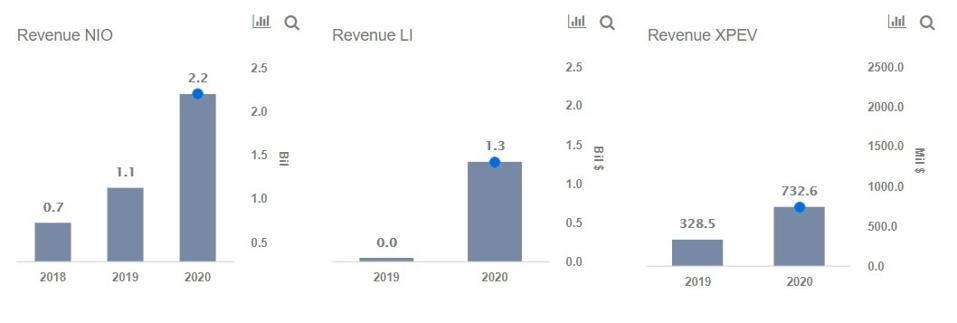
Nio delivered about 21k vehicles in 2019, up from about 11k vehicles in 2018. This compares to Xpeng which delivered about 13k vehicles in 2019 and Li Auto which delivered about 1k vehicles, considering that it began production only late last year. While Nio’s deliveries this year could approach about 40k units, Li Auto and Xpeng are likely to deliver around 25k vehicles with Li Auto seeing the highest growth. Over 2019, Nio’s Revenues stood at $1.1 billion, compared to about $40 million for Li Auto and $330 million for Xpeng. Nio’s Revenues are likely to grow 95% this year, while Xpeng’s Revenues are likely to grow by about 120%. All three companies remain deeply lossmaking as costs related to R&D and SG&A remain high relative to Revenues. Nio’s Net Margins stood at -195% in 2019, Li Auto’s margins stood at about -860% while Xpeng’s margins stood at -160%. However, margins are likely to improve sharply in 2020, as volumes pick up.
Revenue
Valuation
Nio’s Market Cap stood at about $37 billion as of October 28, 2020, with its stock price rising by about 7x year-to-date due to surging investor interest in EV stocks. Li Auto and Xpeng, which were both listed in the U.S. around August as they looked to capitalize on surging valuations, have a market cap of about $15 billion and $14 billion, respectively. On a relative basis, Nio trades at about 15x projected 2020 Revenues, Li Auto trades at about 12x, while Xpeng trades at about 20x.
While valuations are certainly high, investors are likely betting that these companies will continue to grow in the domestic market, while eventually playing a larger role in the global EV space leveraging China’s relatively low-cost manufacturing, and the country’s ecosystem of battery and auto parts suppliers. Of the three companies, Nio might be the safer bet, considering its slightly longer track record, higher Revenues, and investments in technology such as battery swaps and self-driving. Li Auto also looks attractive considering its rapid growth - driven by the uptake of its hybrid powertrains - and relatively attractive valuation of about 12x 2020 Revenues.
Electric vehicles are the future of transportation, but picking the right EV stocks can be tricky. Investing in Electric Vehicle Component Supplier Stocks can be a good alternative to play the growth in the EV market.
See all Trefis Price Estimates and Download Trefis Data here
What’s behind Trefis? See How It’s Powering New Collaboration and What-Ifs For CFOs and Finance Teams | Product, R&D, and Marketing Teams