Small employers are currently experiencing a severe staffing shortage. In March 2021, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported an all-time series high of 8.1 million job openings with a job openings rate of 5.3%. This represents the number of job openings on the last business day of the month as a percent of total employment plus job openings. It was a 43% increase from the year before in March 2020, the month the Covid shutdowns started.
This was illustrated in April’s Small Business Covid-19 survey and NFIB’s Small Business Economic Trends survey. Small employers, representing 11 industries, were asked about staffing shortages and their impact on their businesses. Half of small employers in eight of the eleven industries experienced some type of staffing shortage.
Industries Impacted the Most
Industries that have been hit the hardest were transportation, manufacturing, and construction. Small employers in the “transportation, communication, and public utilities” industry had the largest portion of employers with a “significant” staffing shortage (50%). Additionally, half of the business reported significant loses of sales opportunities due to labor shortages.
Three other industries had over 50% of businesses reporting significant or moderate lost sales opportunities. Fifty-eight percent of small business owners in the construction industry reported significant or moderate lost sales opportunities due to staffing shortages, closely followed by manufacturing and mining (55%) and services (55%) industries.
According to April’s Small Business Economic Trends survey, 22% of all small business owners plan to increase employment to remedy the staffing shortage. At least 20% of business owners in six of the nine industries plan to increase employment. Owners in manufacturing had the highest rate, with 31% of them planning to increase employment. Other industries with high rates of planning to increase employment include transportation (28%) and construction (24%). To succeed, owners are raising compensation to attract and keep employees. Thirty-nine percent of manufacturing firms reported raising compensation in April, followed by 37% of the retail firms and 34% of construction and wholesale firms, all hoping to attract or keep qualified workers..
Forty-three percent of small businesses across all industries have current job openings and are unable to currently fill a position(s). More than half of small business owners in construction (60%), transportation (56%), and manufacturing (50%) reported not being able to fill a position(s).
Industries Impacted the Least
Industries that were impacted the least by staffing shortage were financial, insurance, and real estate (FIRE), wholesale, professional services, and agriculture.
Small employers in the financial, insurance, and real estate (FIRE) industry were the least impacted by the tight labor market, with 77% of them not experiencing a staffing shortage. About one-quarter of small business owners in finance (23%) were unable to fill jobs.
Staffing shortages were also less prevalent in wholesale and professional services industries, with 52% of wholesale and 52% of professional services businesses reporting no staffing shortage. Fifty percent of small employers in wholesale experienced no loss in sales opportunities due to staffing shortages and 25% of employers in professional services were unable to fill jobs.
In addition, small employers in agriculture experienced a minor impact due to staffing shortages, with 42% small employers reporting no staffing shortage. The industry also experienced less severe lost sales opportunities with only 36% of small employers in the industry reporting lost sales opportunities. Only 5% of small businesses in agriculture plan to increase employment, consistent with the industry’s less serious staffing shortage.
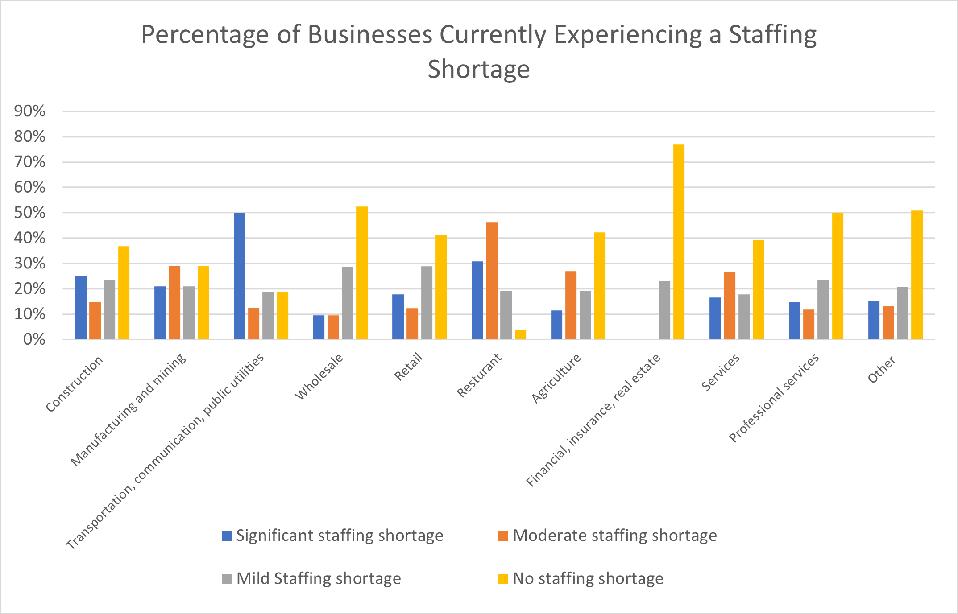
Source: April’s Small Business COVID-19 Survey
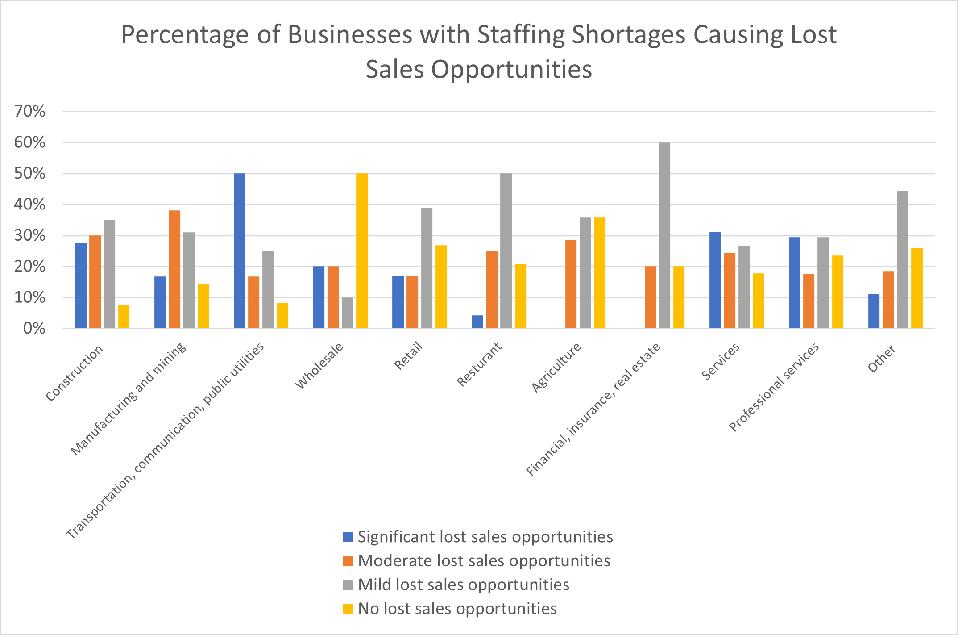
Source: April’s Small Business COVID-19 Survey
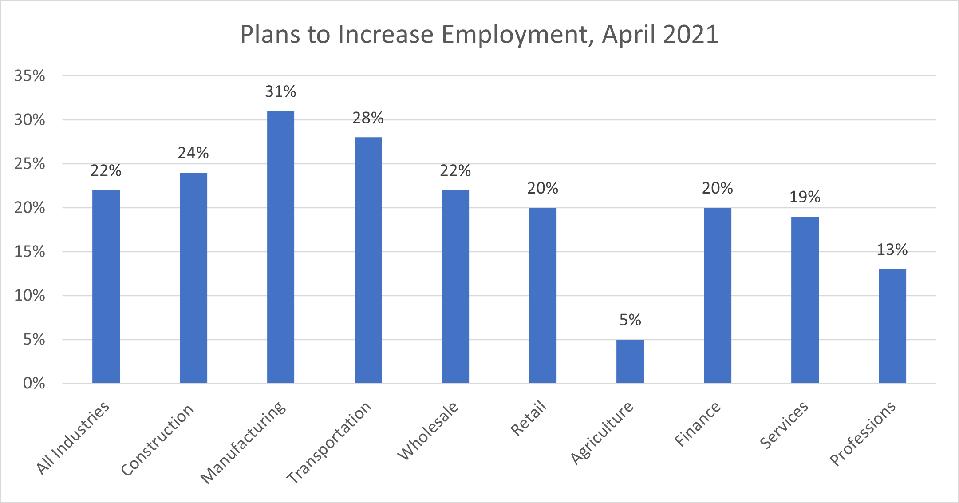
Source: NFIB Small Business Economic Trends Survey
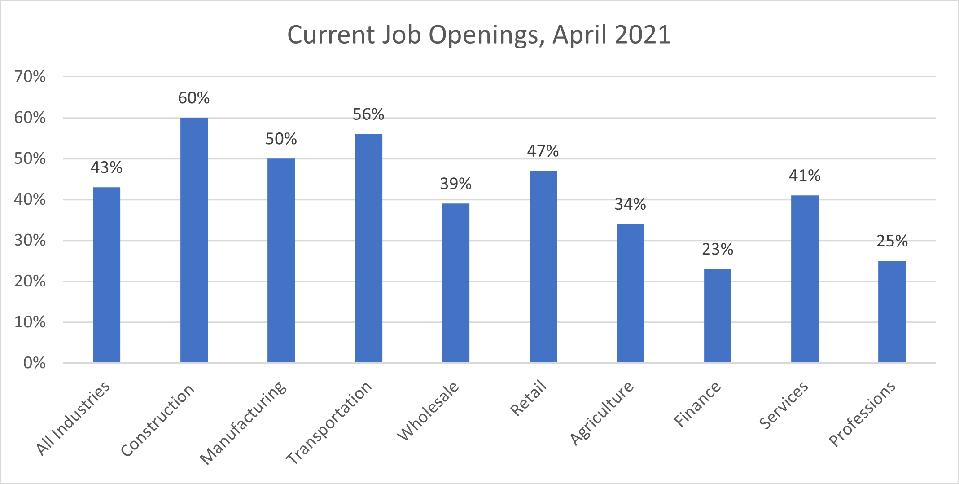
Source: NFIB Small Business Economic Trends Survey



















